Goals of the Dissertation

Introduction
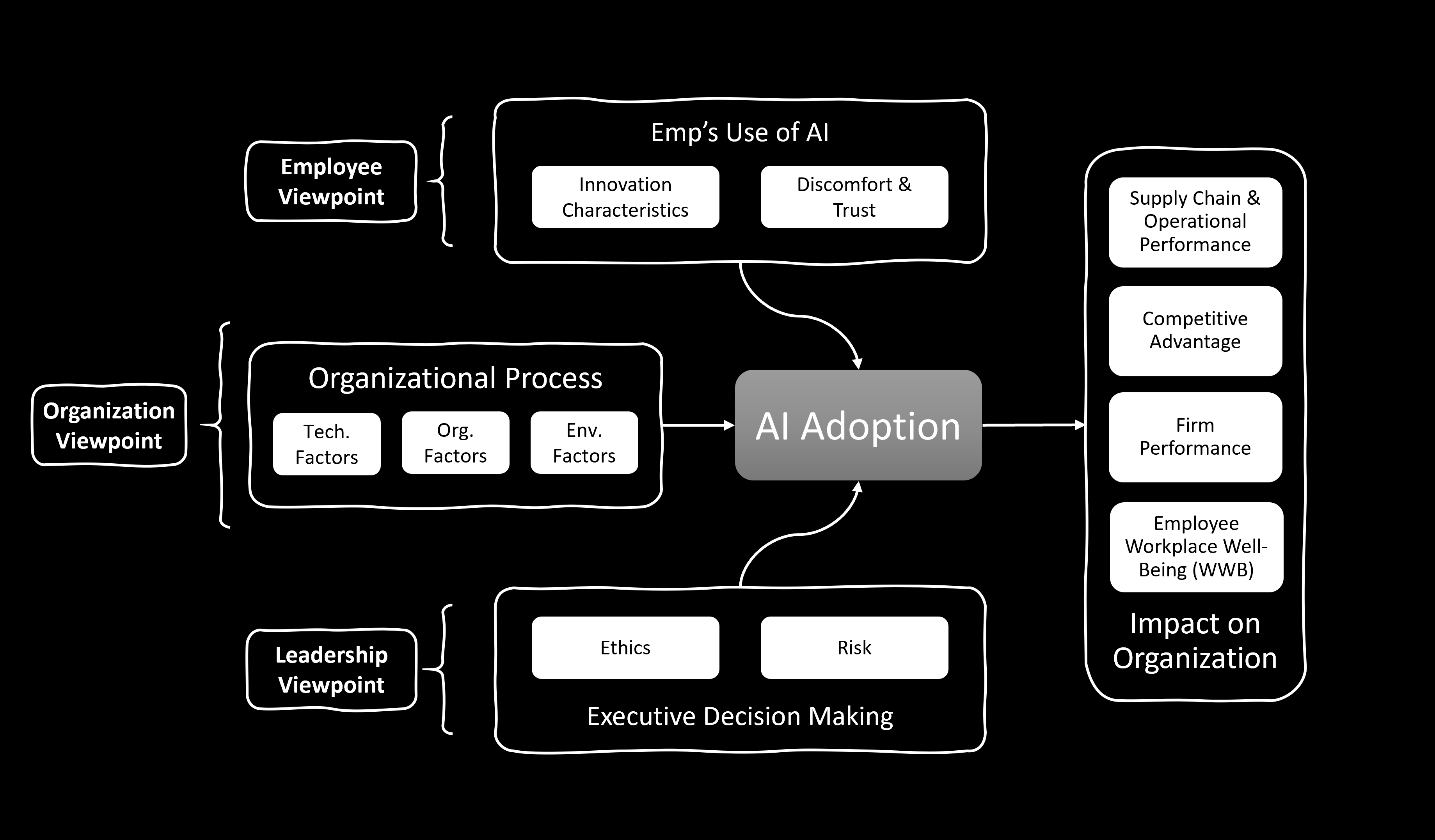
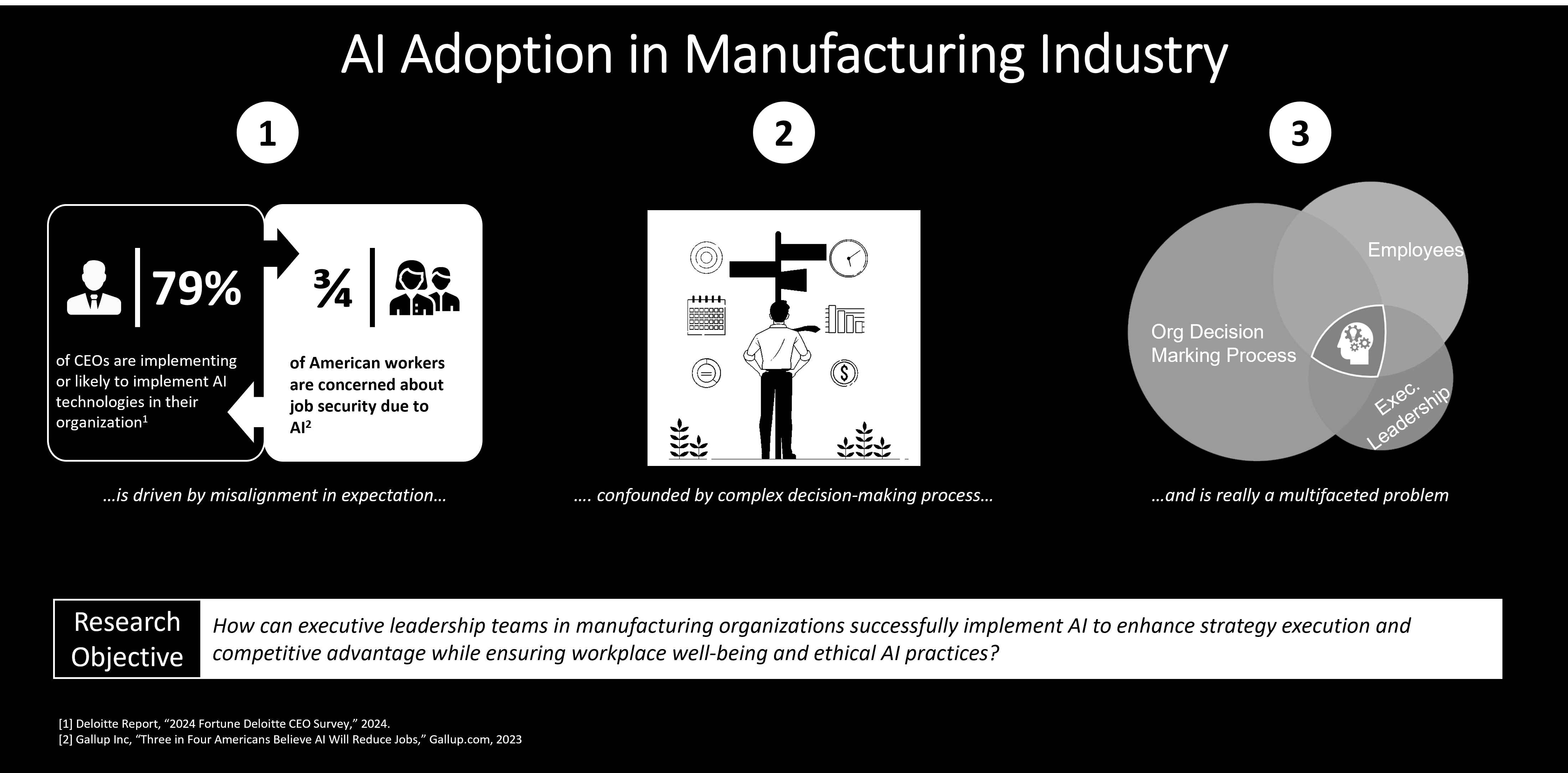
The manufacturing industry is undergoing a significant transformation driven by rapid technological advancements, including AI. A recent survey by Deloitte found that 79% of CEOs are implementing or likely to implement AI to gain a competitive edge in a dynamic and challenging business environment. However, while the strategic benefits of AI adoption are clear, its implementation presents unique challenges as there are multiple stakeholders with differing priorities within organizations. Decision-making in the manufacturing sector is often complex and fragmented, and so executives need to balance the act of integrating AI into the existing management system of the company while minimizing operational disturbance. At the same time, employees frequently express concerns about AI adoption, including issues of trust, discomfort, and fears of job displacement.
Goals
The overarching goal of this dissertation is to explore how executive leadership teams in manufacturing organizations can successfully implement AI to enhance strategy execution and achieve competitive advantage while ensuring workplace well-being and ethical AI practices.